What are mangroves?
Mangroves are ecosystems that you can find on the border between land and sea. They are home to a wide variety of species, including migratory birds, marine species, reptiles, and some plant species. In addition, they have many benefits, such as their contribution to food security and the protection of coastal communities around the world.
Take a 3D tour of the Mangle ecosystem!
What species are there?
- Red mangrove (Rhizophora mangle)
- Black mangrove (Avicennia germinans)
- White mangrove (Laguncularia racemosa)
- Button mangrove (Conocarpus erectus)
These four mangrove species are categorized as protected species in the List of Threatened Species of Guatemala (LEA, Lista de Especies Amenazadas de Guatemala by its acronym in Spanish).
Where can you find mangroves?
In Guatemala, the mangrove ecosystem is distributed on the Pacific and Caribbean coastline, representing an area of 25,089 hectares.
They are located in important protected areas such as Bocas del Polochic, Río Sarstún, Bahía de Santo Tomas, Punta de Manabique, Río Dulce in Izabal. About the Pacific mangroves we can mention various places such as Manchón Guamuchal, the Monterrico Multiple Use Natural Reserve, Sipacate-Naranjo National Park, Hawaii, and other areas such as Las Lisas and La Barrona.
(CONAP, 2020)
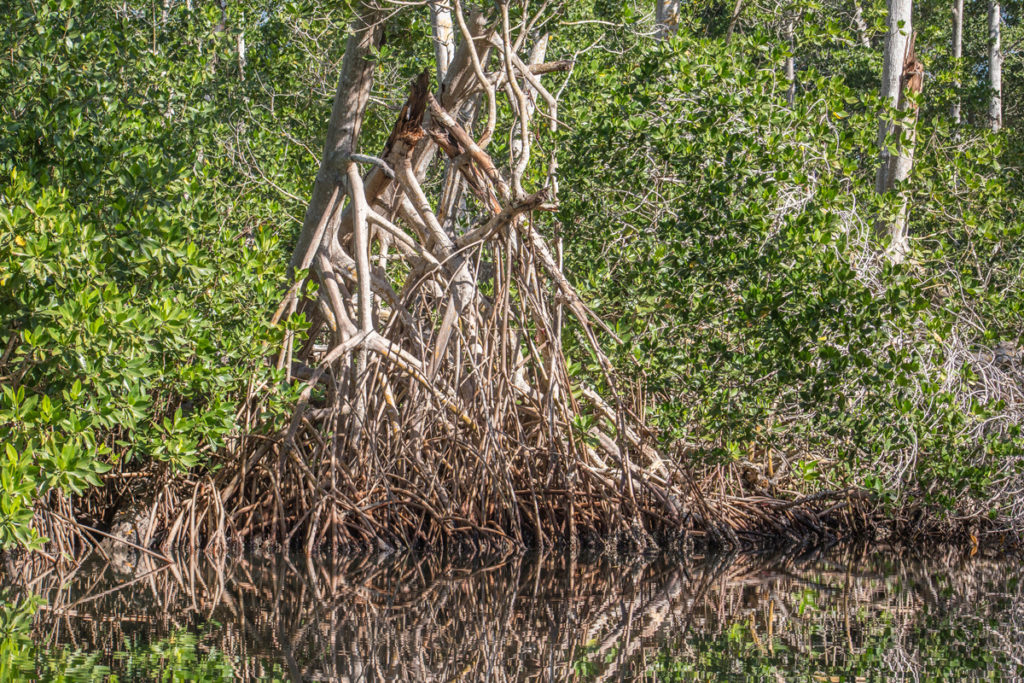

Rhizophora mangle, red mangrove, Manchon Guamuchal, Retalhuleu, Febrero 1 2018, Melanny Quiñonez
Why are mangroves so important?
Mangroves are one of the most productive ecosystems in the world. It gives us multiple benefits, for example:
- The mangrove is used for the construction of roofs and houses.
- Living barriers that serve as a natural coastal defense against storm surges, tsunamis, sea-level rise, and erosion.
- Serve as a “nursery” or refuge for the young of a large number of species. They maintain rich biodiversity.
- Regulate the weather.
- Preserve water quality.
Educational material
Get to know the mangrove ecosystem through a video
Download the mangrove coloring sheets from Semillas del Océano page.